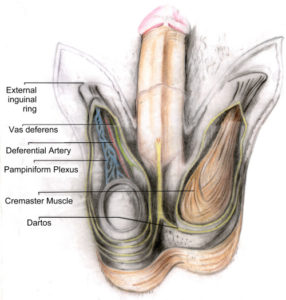
Theory of Cremesteric Compartment Complex:
The spermatic cord and its structures ( vas deferens, testicular artery, pampiniform plexus of testicular veins, lymphatics) are encircled by the cremasteric muscle and fascia.
The encircling cremasteric muscle creates a tight compartment around the structure of the spermatic cord.
This leads to venous stasis and secondary venous dilatation and tortuosity. According to this theory, it is ‘venous stasis’ and not ‘venous reflux’ that leads to the effects of varicocele. The surgical approach which releases this cremasteric entrapment should be the most ideal approach.